
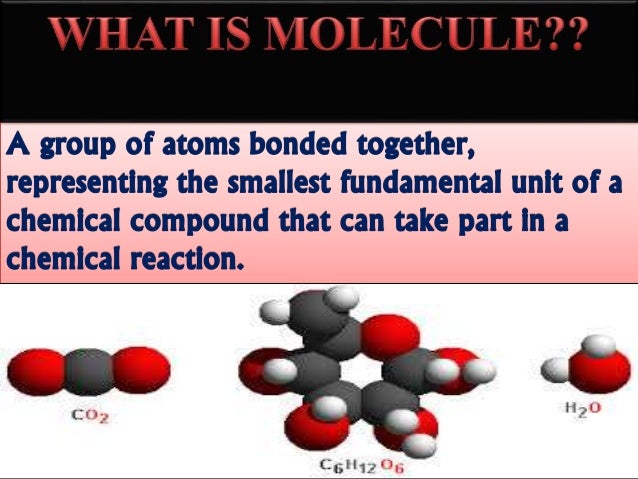
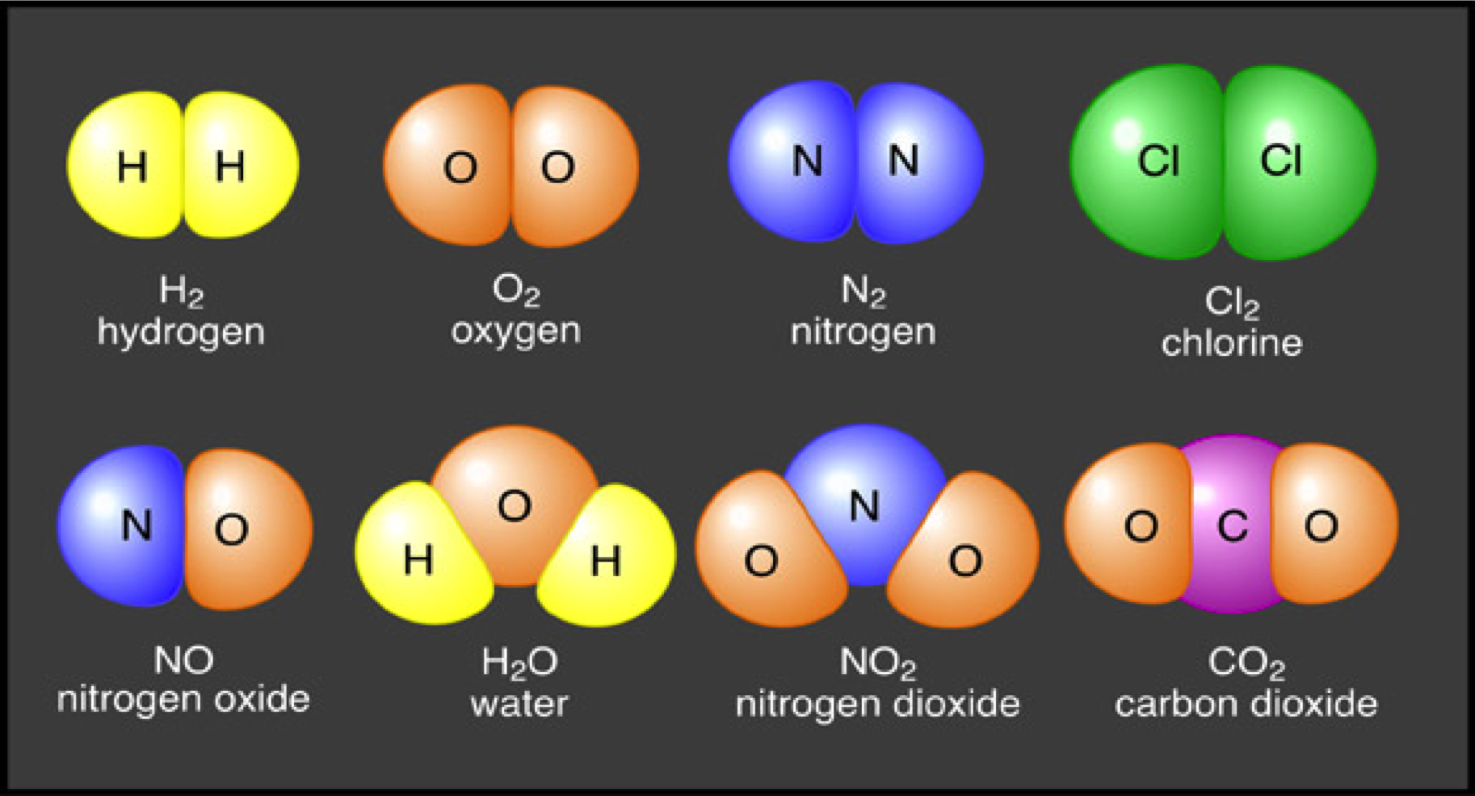
A triple covalent bond means that three pairs of outer shell electrons are shared between the two atoms.Ĭovalent bonds between atoms are strong. A double covalent bond means that two pairs of outer shell electrons are shared between the two atoms. A single covalent bond means that a single pair of outer shell electrons is shared between the two atoms. Ĭovalent bond: a chemical bond between two or more identical or non-identical atoms that involves s haring of a pair (or pairs) of outer shell electrons. There are two main types of chemical bond within a molecule ( intramolecular forces) that holds a molecule together: covalent and ionic. What types of chemical bond exist between atoms in a molecule?Ī chemical bond involves the sharing or transfer of outer shell (valence) electrons between atoms in a molecule. Use this definition for A level Chemistry. A molecule contains ≥2 identical or non-identical atoms, bonded together by covalent bonds, and may be electrically neutral or an electrically charged ion: MOST SCIENTISTS AGREE WITH THIS DEFINITION. Use this definition for GCSE Chemistry.Ģ. A molecule contains ≥2 identical or non-identical non-metal atoms, bonded together by covalent bonds, and must be electrically neutral: ALL SCIENTISTS AGREE WITH THIS DEFINITION. There is considerable debate in relation to the correct definition of the term “molecule”. *Controversy in the definition of the term ‘molecule’ Another example is the fractional distillation of crude oil different alkane hydrocarbon molecules (such as diesel, fuel oil and naphtha) present in the crude oil mixture are separated by virtue of their differences in boiling (and therefore condensation) points in a fractionating tower. An example is a solution of salt water: the salt (sodium chloride) can be separated from the water by evaporation. A molecule may therefore be an element or compound that is covalently bonded.Ī mixture is substance made up of any combination of elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded together and may, in general, be separated by physical processes (such as distillation or filtration) into its constituent elements or compounds. It is difficult to separate a compound into its constituent elements as the process requires disruption of covalent or ionic chemical bonds.Ī molecule* contains ≥2 identical or non-identical non-metal atoms covalently bonded together that is overall electrically neutral (not a positively- or negatively-charged ion). However, the situation is far more complex as some covalent molecules exist as charged ions and these ions may ionically bond with other groups of oppositely charged ions. Two types of compound exist: covalent molecule or ionic compound. hydrogen H 2 molecule and sulfur S 8 are polyatomic elements).Ī compound is substance where two or more different atoms or ionsare chemically bonded together. Whereas, a polyatomic element, has a multiple atom repeating unit (e.g. copper, sodium or helium) repeating unit. A monatomic element has a single atom (e.g. Matter is made up of repeating units of atoms, molecules or ions.Īn element is a substance that contains only one type of atom as its repeating unit. What are the relationships between atom, element, molecule, ion, compound and mixture? Classification, variation, food webs and pyramids.Combustion reactions and impact on climate.Atoms elements compounds and mixtures (interactive).B1.6 Waste materials from plants and animals.
RSC Learn Chemistry Classic Chemistry Experiments.RSC Classic Chemistry Experiments (1995).Practical Chemistry (Nuffield Foundation/RSC).3.15 Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.3.14 Organic synthesis and analysis (A2).2.6 Reactions of ions in aqueous solution.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
